In meter equipment, there are three different types of bypass: Horn Bypass, Lever Bypass, and Test Block Bypass.
Horn Bypass
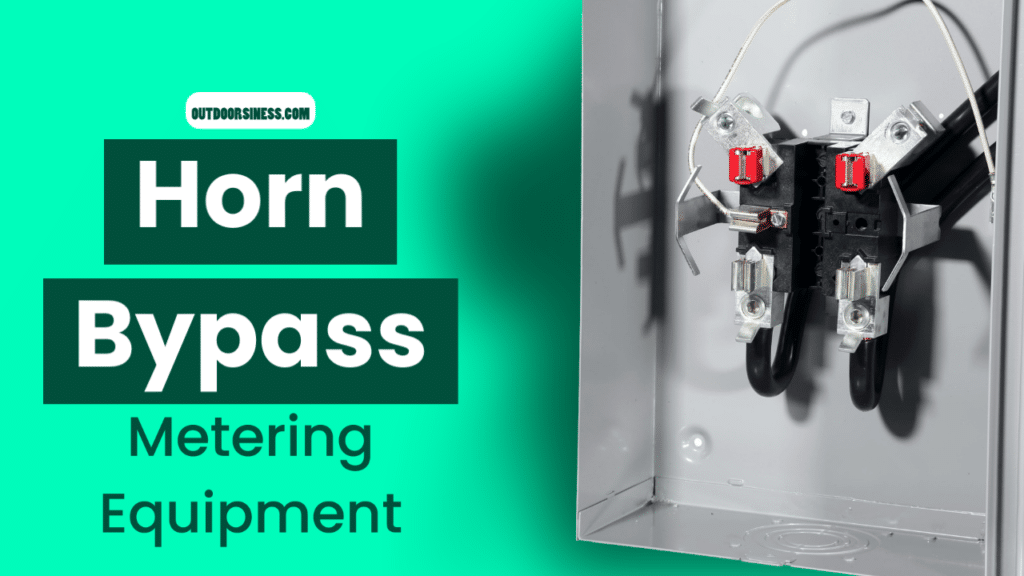
Horn Bypass is used with ringless-style, single-phase out metering equipment. When the outer ringless cover is removed from the meter socket, short bus connectors extend upward from the line side and downward from the load side meter socket jaws, giving the appearance of “horns.” A qualified service technician manually installs one jumper cable per phase using utility supplied jumper cables. This creates a path for current to flow once the meter is removed from the socket. This temporary bypass feature allows the utility to perform meter maintenance without interrupting service to the downstream occupant.
Lever Bypass
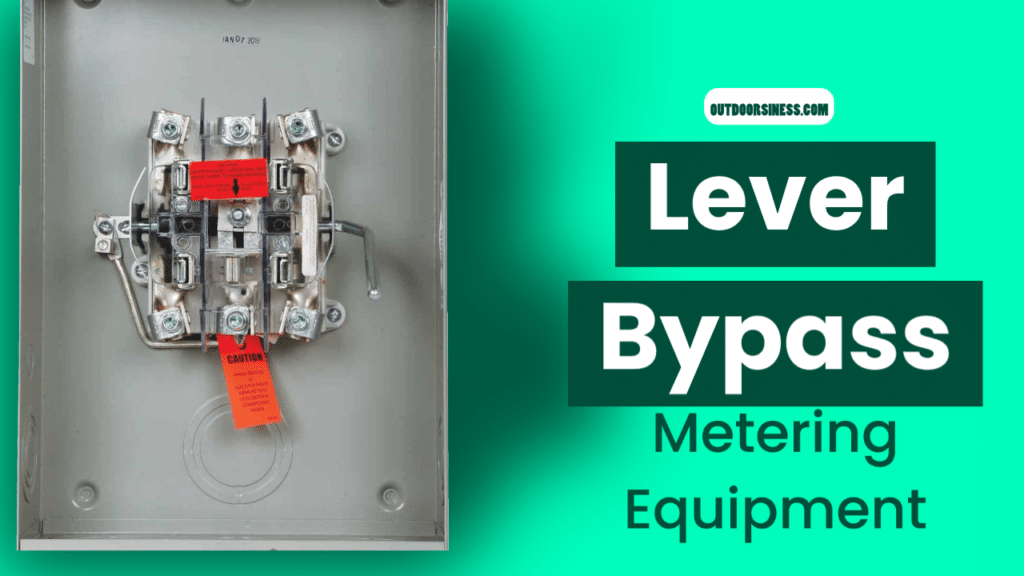
Lever Bypass is used with ringless-style single or three-phase metering equipment. It is supplied with a swing arm or “lever” extending from the right side of the meter socket. When the ringless meter socket cover is removed, the dual-function lever may be manually rotated upward to engage bypass rotor blades into line and load bypass jaws, allowing current to flow through the meter socket with the meter in or out of the socket. The lever also provides a jaw release function. By rotating the lever up as far as possible, the spring-loaded meter socket jaws are spread open for ease of meter installation or removal. This temporary bypass feature allows the utility to perform meter maintenance without interrupting service to the downstream occupant.
Block Bypass
Test Block Bypass is used with ring-style single or three-phase metering equipment and is developed for use along the west coast governed by the Electrical Utility Service Equipment Requirements Committee (EUSERC). Trained service technicians perform meter maintenance while this equipment remains energized and while their meter remains installed in the ring-style meter socket. The “test block” cover is removed, and the technician manually installs a set of jumpers extending from the line to load side connectors feeding to and from the meter being tested. Once the jumpers are in place, bronze current-carrying flat washers are removed from each phase, and at this point, the meter is bypassed or isolated from the circuit. This temporary bypass feature allows the utility to perform meter maintenance without interrupting service to the downstream occupant.
In summary, meter equipment can make use of three different types of bypass: Horn Bypass, Lever Bypass, and Test Block Bypass. Each type serves a unique purpose and is designed to facilitate meter maintenance without interrupting service to the downstream occupant. Understanding the distinctions of these bypass types is essential for qualified service technicians working with metering equipment to perform maintenance and repairs safely and effectively. By utilizing these temporary bypass features, utility companies can conduct meter maintenance efficiently and effectively while ensuring that the customer’s electrical service remains uninterrupted.






